Application Note 173: Label-Free Kinetic Analysis of Carbonic Anhydrase IX Inhibitors on Live Suspension Cells Using Surface Plasmon Resonance Microscopy
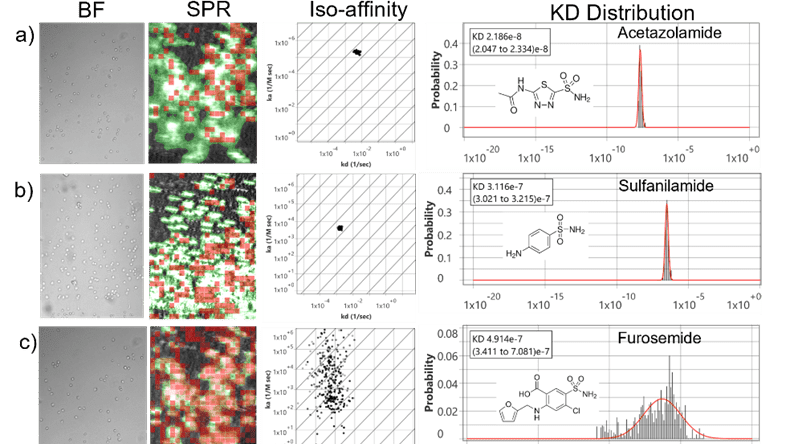
Transmembrane carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX) is a zinc metalloenzyme and overexpressed in numerous cancers and represents an attractive therapeutic target due to its limited expression in normal tissues and …
Application Note 172: Affinity and Avidity Kinetic Binding Analysis Using SPRM
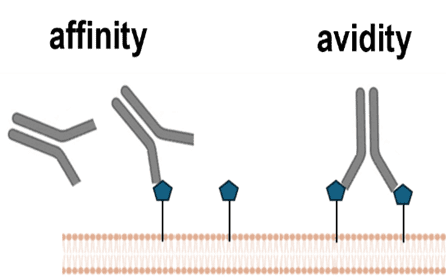
Surface Plasmon resonance microscopy (SPRM) enables high-resolution evaluation of the kinetic binding heterogeneity on whole single cells, without disrupting the native environment of the target. This capability permits measurement in …
Application Note 170: Simultaneous Kinetic Analysis of HER2 Binding in Pancreatic and JIMT-1 Cancer Cells Using SPRm 220
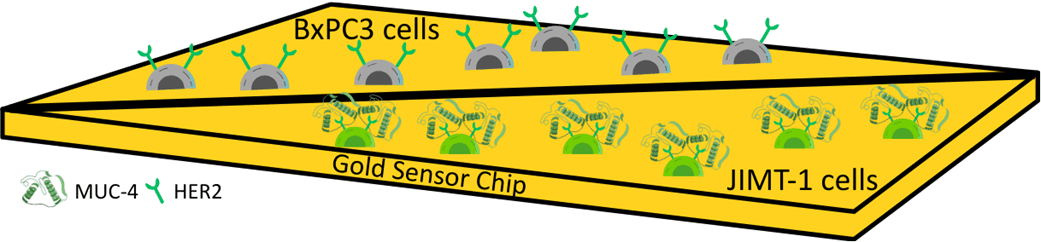
HER2 (Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2) is an important therapeutic target in different types of cancer because it functions to advance tumor development and growth.1 Antibody-based drugs such as …
Application Note 169: Simultaneous Kinetic Binding Analysis of Anti-Mucin-4 on Pancreatic Cancer and HEK293T Cells Using Two-well SPR Microscopy Chip
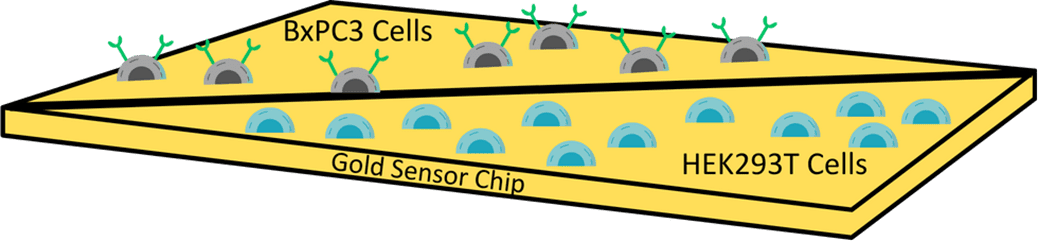
Mucin 4 (MUC4) is a highly glycosylated cell surface protein that is highly overexpressed in cancerous cells of the pancreas, including the BxPC3 cell line. 1, 2 Due to its tumor-specific expression and cell surface localization, MUC4 is …
Application Note 167: Label-Free Characterization of Antibody-Receptor Interactions on Live Suspension Cells using SPRM
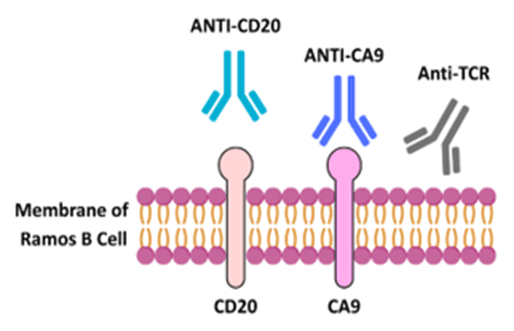
Antibody drug development is emerging as the cornerstone of modern therapeutics, particularly in the realm of immunotherapy. Antibodies have demonstrated great efficacy in treating B-cell cancers by taking advantage of …
Application Note 165: Spatially Resolved Detection of Electroactive Biological Systems Using EC-SPR Microscopy
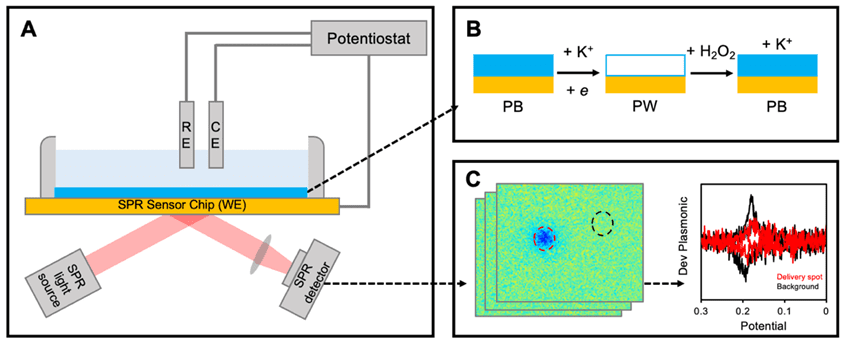
Traditional electrochemical (EC) techniques typically quantify averaged responses from a collection of individual elements and molecules on the surface of electrode.1 These approaches, while effective for bulk analysis, often overlook …
Application Note 163: Binding Activities of Yohimbine Analogues on ADRA2A Overexpressing Live Cells
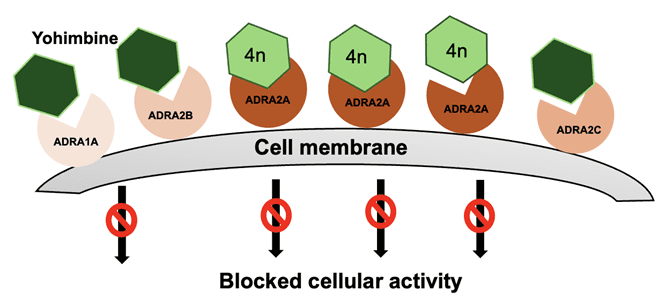
Millions of sepsis-related deaths are reported every year, which makes acute septic shock one of the leading causes of death in intensive care units around the world.1 Septic shock is …
Application Note 162: N-linked Glycan Deglycosylation Unmasks New HPA O-linked Glycan Heterogeneity
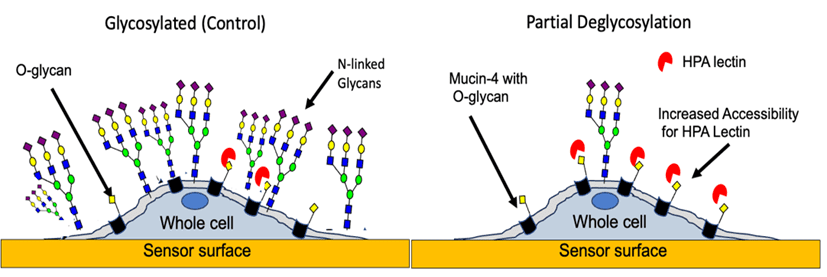
Most membrane proteins carry some form of glycans, which regulate many cellular processes such as cell differentiation and cell-to-cell interactions.1 There are two types of glycans based on the type …
Application Note 160: Influence of Aberrant Glycosylation on the Binding Capability of Muc-4 in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
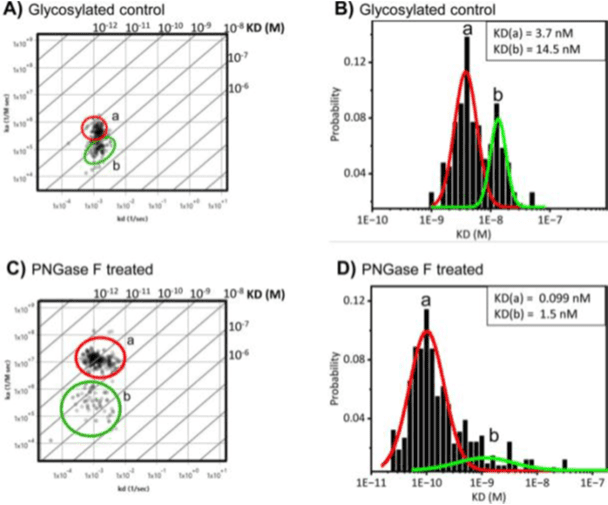
Mucin-4 (Muc-4) is a heavily glycosylated membrane glycoprotein which is associated with pancreatic cancer and metastasis.1 This glycoprotein primarily has O-glycans which contributes to its bulky structure in the extracellular …
Application Note 159: Real-Time Monitoring of Glycan Heterogeneity in Cancer Cells
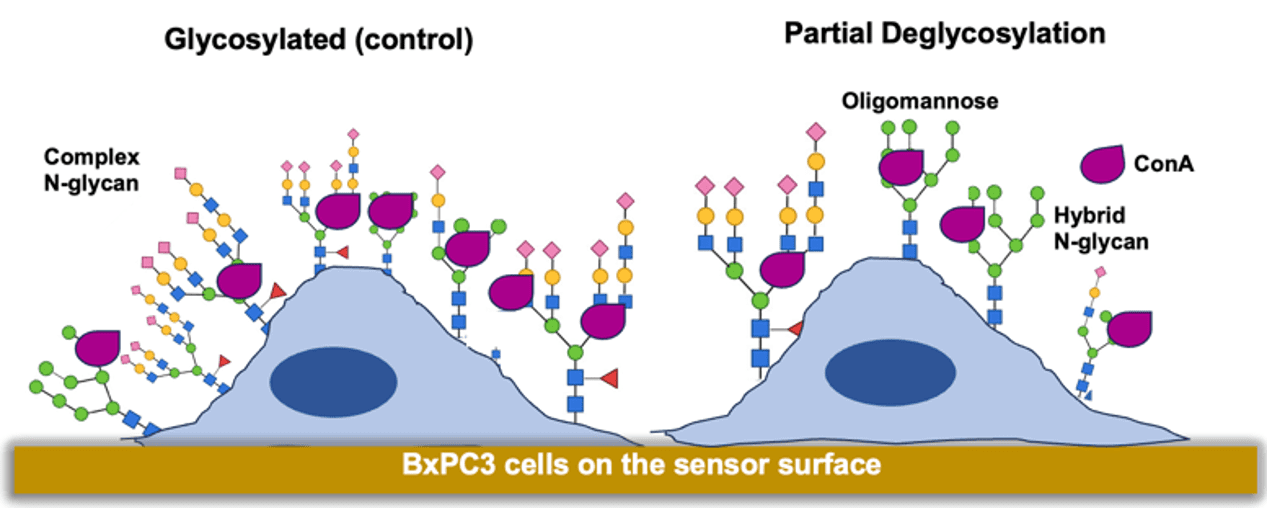
Membrane proteins are the main targets of therapeutic drugs and most of them carry some form of glycan structures, which play pivotal roles in protein folding, stability, cell communication, cell …
