Application Note 173: Label-Free Kinetic Analysis of Carbonic Anhydrase IX Inhibitors on Live Suspension Cells Using Surface Plasmon Resonance Microscopy
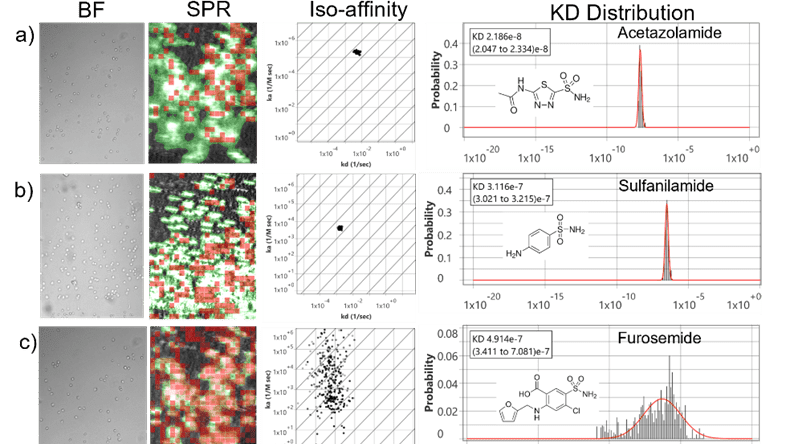
Transmembrane carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX) is a zinc metalloenzyme and overexpressed in numerous cancers and represents an attractive therapeutic target due to its limited expression in normal tissues and …
Application Note 172: Affinity and Avidity Kinetic Binding Analysis Using SPRM
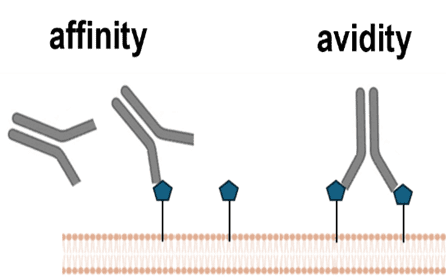
Surface Plasmon resonance microscopy (SPRM) enables high-resolution evaluation of the kinetic binding heterogeneity on whole single cells, without disrupting the native environment of the target. This capability permits measurement in …
Application Note 171: Probing the Role of Dissolved CO₂ in Electrochemical Interfaces via EC SPR

Carbon dioxide (CO₂) capture is a key approach to addressing the present climate crisis because of over emission of greenhouse gases. As the dominant human-made cause of global warming, CO₂ …
Application Note 170: Simultaneous Kinetic Analysis of HER2 Binding in Pancreatic and JIMT-1 Cancer Cells Using SPRm 220
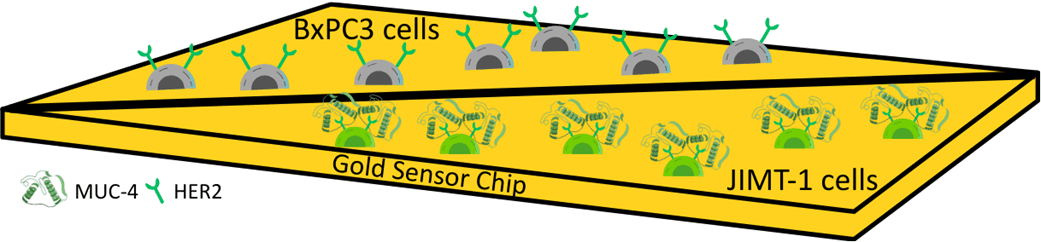
HER2 (Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2) is an important therapeutic target in different types of cancer because it functions to advance tumor development and growth.1 Antibody-based drugs such as …
Application Note 169: Simultaneous Kinetic Binding Analysis of Anti-Mucin-4 on Pancreatic Cancer and HEK293T Cells Using Two-well SPR Microscopy Chip
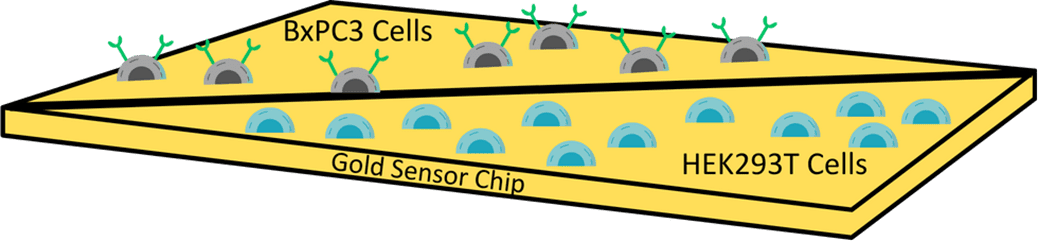
Mucin 4 (MUC4) is a highly glycosylated cell surface protein that is highly overexpressed in cancerous cells of the pancreas, including the BxPC3 cell line. 1, 2 Due to its tumor-specific expression and cell surface localization, MUC4 is …
Application Note 168: Enhanced SPR Detection of Small Molecules and Bacterial Markers Using Directionally Immobilized Aptamers on Engineered Nanoplatforms
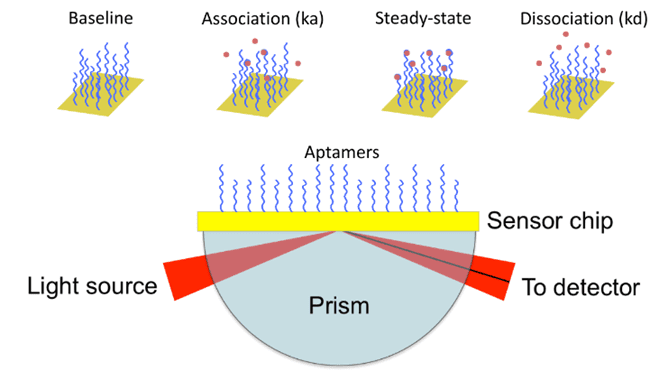
Aptasensors have rapidly become informative tools in modern diagnostics due to their fast response, excellent specificity, and readability for a large range of complex samples. Biosensors exploit the unique molecular …
Application Note 167: Label-Free Characterization of Antibody-Receptor Interactions on Live Suspension Cells using SPRM
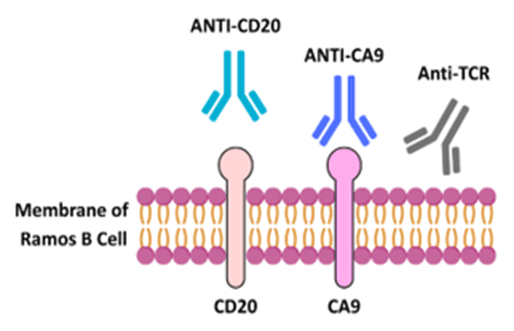
Antibody drug development is emerging as the cornerstone of modern therapeutics, particularly in the realm of immunotherapy. Antibodies have demonstrated great efficacy in treating B-cell cancers by taking advantage of …
Application Note 166: Probing Redox Interactions Between Microbial EPS and p-Nitrophenol Using Electrochemical Surface Plasmon Resonance
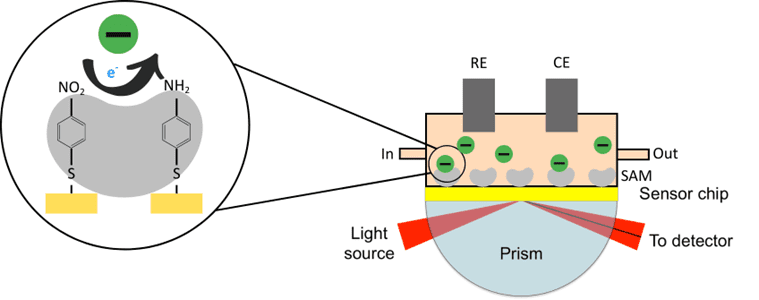
Microbial extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) with redox functional groups play a vital role in the bioconversion of pollutants, which can affect their reactivity toward diverse environmental pollutants. However, the redox …
Application Note 165: Spatially Resolved Detection of Electroactive Biological Systems Using EC-SPR Microscopy
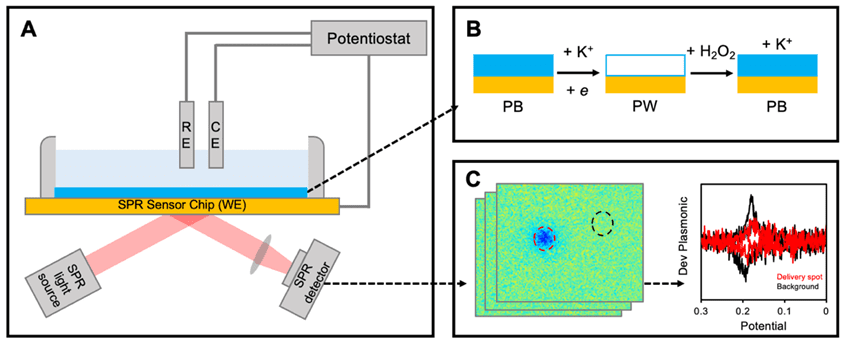
Traditional electrochemical (EC) techniques typically quantify averaged responses from a collection of individual elements and molecules on the surface of electrode.1 These approaches, while effective for bulk analysis, often overlook …
Application Note 164: Simultaneous Analysis of Binding Interactions using Multi-Channel SPR
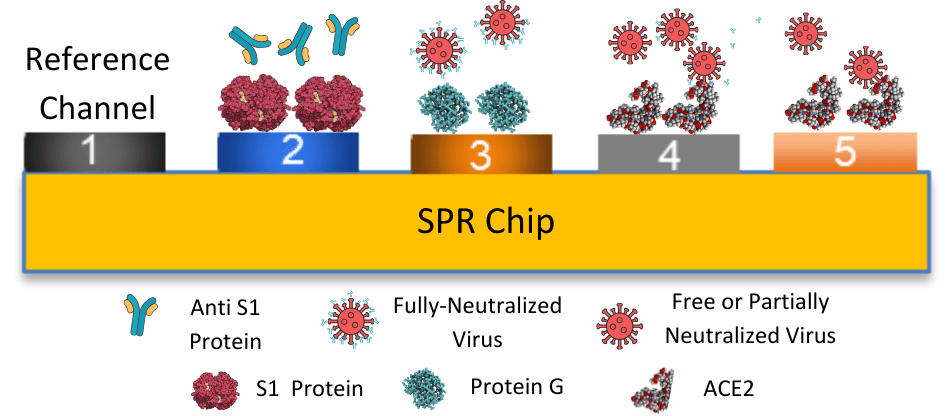
Entry level surface plasmon resonance (SPR) tools with dual channels have only one measurement point since the other channel is always used as a reference.1 Therefore, increasing efforts have been …
