Application Note 142: Small Molecule Binding to Membrane Transporter Using SPRm200
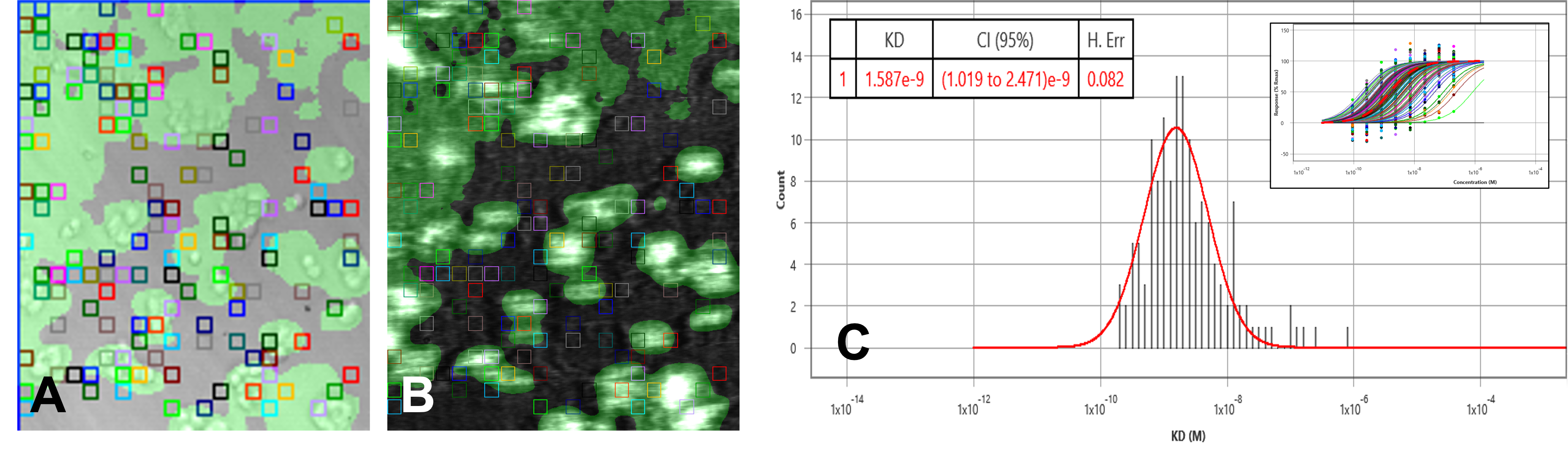
Transporters are large proteins (40–200 kDa) located in the plasma membrane of cells and organelles. They normally span the membrane many times and modulate the transfer of xenobiotics (including nutrients, micronutrients and pharmaceuticals), and endogenous substances such as neurotransmitters, hormones, signaling molecules, vitamins across cellular membranes, tissues or organ barriers.
Application Note 141: SPRM Measurements of Binding Kinetics between Rituximab and CD20 on Live B Cells

Cell-based immunotherapy has gained great attention from researchers and pharmaceutical companies, particularly due to its promise to treat various cancers. Understanding the interaction between drug candidates and targets on the cell membrane is crucial to drug development.
Application Note 140: Membrane Transport Protein Binding Kinetics Using Label-Free SPRm200
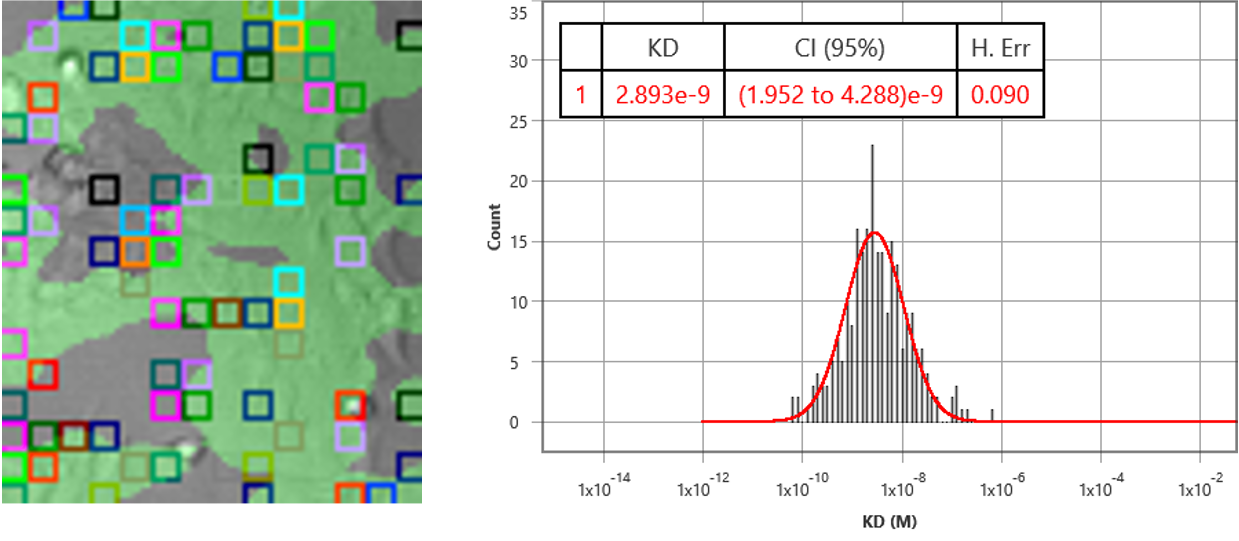
In this application note, binding interactions of an antibody to a membrane transport receptor were studied using SPRm 200. Transporters have important roles in physiological processes ranging from cellular uptake of nutrients to the absorption of drugs. Despite their importance as a drug discovery, it is difficult to determine its function: direct biophysical studies require these proteins be solubilized and purified and between their extraction and reconstitution, transport activity cannot be measured because of the lack of a vectorial environment.
Application Note 139: Single-Injection Kinetic Measurement Technique for Studies of COVID-19 S1 Protein and ACE2 Binding
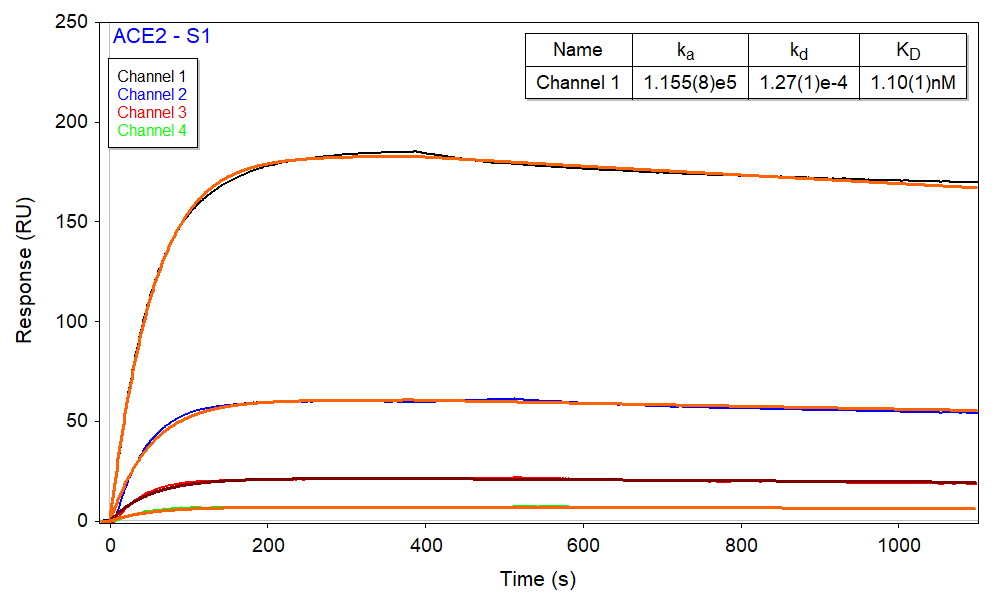
This application note shows the application of the single-injection measurement technique in binding kinetic studies between COVID-19 S1 and ACE2 proteins. The five-channel SPR instrument, with the BI-DirectFlow™ technology, provides a unique multi-channel technique for precise sample delivery and high-quality measurement.
Application Note 138: Kinetic Measurement of COVID-19 S1 Protein and ACE2 Binding
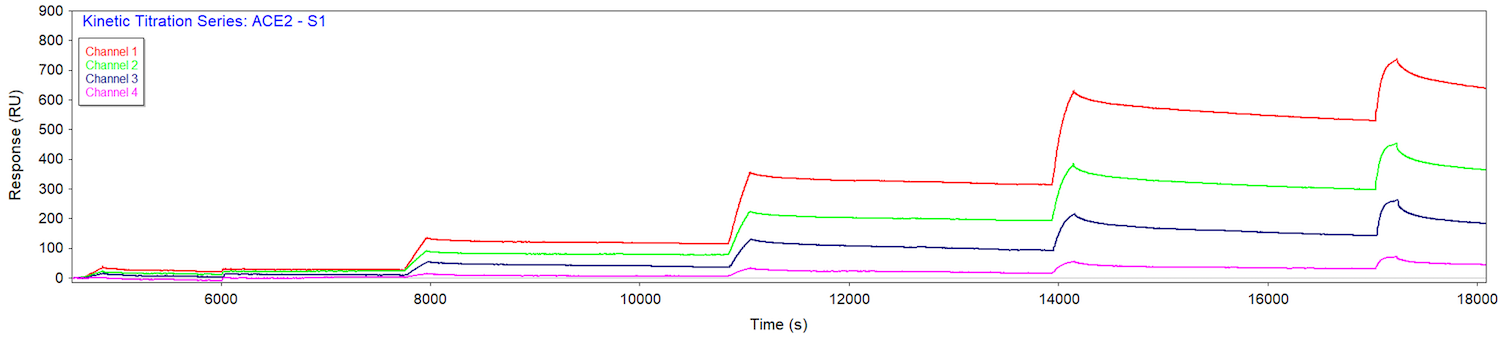
The coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic continues to evolve. This disease is caused by the highly contagious coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and is initiated by the viral invasion into host cells through viral attachment to angiotensin (Ang)-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). ACE2, expressed in numerous different tissues, is the receptor through which the COVID-19 spike-protein (S-protein) gains entry into cells for subsequent viral replication.
Application Note 137: Ginnalin A and Tabersonine Inhibition of Amyloid β(1-42) Aggregation
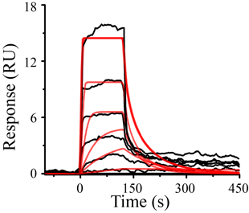
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is currently ranked as the sixth leading cause of death in the United States and is the most common neurological disorder. Production and accumulation of amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptides in the brain are a hallmark of AD. Among Aβ peptides of different lengths, Αβ(1-42) has the highest propensity to aggregate.
Application Note 136: Sensitivity and kinetic analysis of carboxyl-graphene oxide-based SPR biosensors for label-free detection of lung cancer biomarker
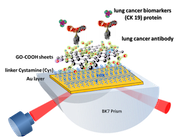
This work demonstrates the excellent potential of highly sensitive carboxyl-graphene oxide (carboxyl-GO) based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) immunosensor for the detection of lung cancer for cytokeratin 19 biomarker in human …
Application Note 135: Measuring Binding Kinetics in Cell Medium with SPRM
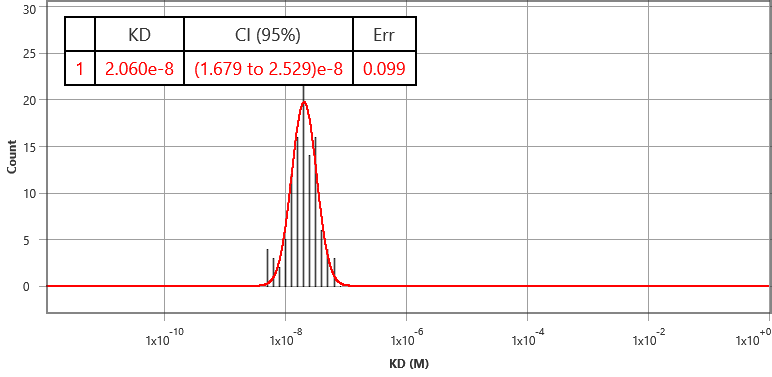
Fixation of cells is a convenient and routinely used method by many labs to study cells. However, fixation may alter certain types of protein receptors, thus affecting their binding kinetics. …
Application Note 134: Positive and Negative Control Studies of Small Molecule Binding to Membrane Protein
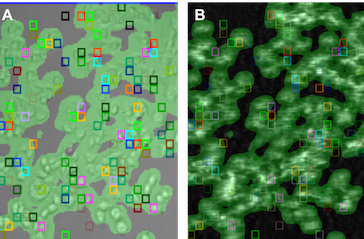
SPR microscopy (SPRm) has emerged as a unique tool for measuring the affinity and kinetics of ligand binding to membrane proteins on the cells directly. The technology integrates the traditional …
Application Note 133: Interaction of Protein Phosphatase 1 with its Muscle Glycogen– targeting Regulatory Subunit Measured by SPR
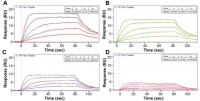
Glycogen is the primary storage form of glucose. Glycogen synthesis and breakdown are tightly controlled by glycogen synthase (GYS) and phosphorylase, respectively. The enzyme responsible for the process is protein …
