Application Note 129: AZ1395 small molecule targeting GPR39
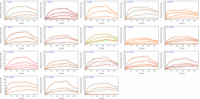
Membrane proteins play critical roles in cellular communications and are the most popular drug targets, accounting for over a half of the FDA approved drugs. One particularly important example of …
Application Note 128: SPR Microscopy for Acid-Sensing Ion Channels
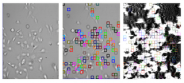
Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) are voltage independent cation channels, which are expressed in both central and peripheral neurons.[1] Four genes that encode six ASIC subunits have been identified in mammals …
Application Note 127: Quantifying Antibody Binding to Membrane Proteins on Single Cells with SPR Microscopy
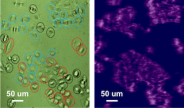
Monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapies have become established methods for treating cancer, autoimmune disorders, asthma and many other diseases. MAb drugs represent approximately half of the total sales of all biopharmaceutical …
Application Note 126: GPCR Binding Assays with SPR Microscopy
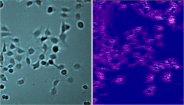
G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR) are integral membrane proteins that transmit signals from external stimuli to the cell interior. They play key roles in many cellular processes, such as sensorial, hormonal, …
Application Note 125: Lectin-Glycoprotein Interactions with SPR Microscopy
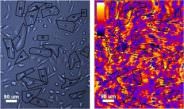
Membrane proteins are involved in many biological processes, such as signaling between cell’s internal and external environments, transport of ions and molecules and catalysis of chemical reactions [1] and they …
Application Note 124: Quantifying Molecular binding to Membrane Proteins on Individual Cells with Surface Plasmon Resonance Microscopy
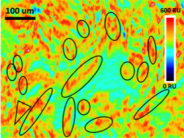
SPRm 200 System is the world’s first commercial Surface Plasmon Resonance Microscopy (SPRM). It combines the high spatial resolution of optical microscopy with the powerful sensing capability of SPR, making …
Application Note 122: Surface Plasmon Resonance Microscopy for Multiple and Single Cell Membrane Binding Kinetics Studies
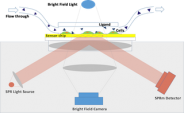
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) is a powerful technique for measuring the binding kinetics of biomolecular interactions in a real-time and label-free manner [1]. In traditional SPR assays, the target molecule is extracted and purified from the cell and immobilized onto the sensor surface for measurement of the interaction kinetics between the target and the drug candidate.
