Application Note 117: Real-time Monitoring Biomarker Expression of Carcinoma Cells
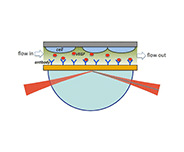
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is an angiogenic signal protein biomarker produced by oxygen-hungry cells to stimulate the growth of blood vessels.[1] It binds to specialized receptors on the surfaces of endothelial cells and directs them to grow new blood vessels during embryonic development. Certain types of tumor cells produce abnormally large amounts of VEGF or block the action of angiogenesis inhibitors
Application Note 116: Temperature Dependence of Enzymatic Cleaving Activity
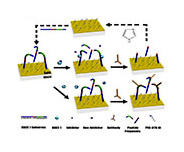
Some biomolecules such as enzymes can exhibit much greater biological activities at physiological temperature (37.5 °C) or higher (e.g., DNA polymerase). The focus of this study is to screen for potential inhibitors of β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1). BACE1 is an enzyme that cleaves the transmembrane amyloid precursor protein to produce the amyloid beta
Application Note 115: SPR Assay of Clinical Alzheimer Disease Samples: Amyloid β Peptides in Cerebrospinal Fluids
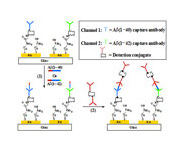
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder, affecting over 6.5 million people over the age of 65 in the U. S. In the senile plaques of AD patient’s brain, the major components are peptides composed of 39–43 amino acid residues (referred to as the amyloid β or Aβ peptides).[1-2] One of the hypotheses for AD neuropathology is that the misfolding and subsequent aggregation of these peptides
Application Note 114: SPR Binding Affinity Determination of Novel Peptide Inhibitors to the Innate Immune activator C1q
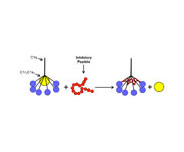
The complement system is an essential component of the human innate immune system, playing a critical role as a defense mechanism against invading pathogens, priming adaptive immune responses and helping to remove immune complexes and apoptotic cells. Three different pathways comprise the complement system: the classical, lectin and alternative pathways [1]. While the complement system plays a central role
Application Note: 113 – Flow-Through Electrochemical Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR): Detection of Intermediate Reaction Products
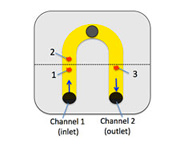
SPR is sensitive to various processes taking place on or near a sensor chip. The SPR sensor chip can also simultaneously serve as a working electrode for electrochemical measurements. Combining electrochemical with SPR measurements has led to the development of Electrochemical SPR (EC-SPR). To date, EC-SPR has been used in the analysis of trace metal ions, detection of surface bound redox species, electrochemical polymerization
Application Note: 112 – Detection of Wild-Type and Mutant p53 Proteins in Cancer Cell Lysates
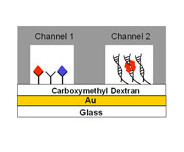
This application note describes the simultaneous SPR detection of wild-type and mutant p53 proteins in cancer cell laysates. p53 is a transcription factor (i.e., DNA-binding protein) that plays an important role in DNA repair and tumor suppression by inhibiting the growth of tumor cells through eliciting either cell-cycle arrest or apoptosis [1-3]. In solution, p53 molecules tetramerize at their C-termini and the resultant p53 tetramer can bind
Application Note: 111 – Measuring Surface Charge Density: A New Application with SPR
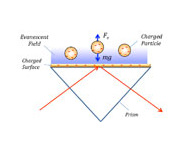
Surface charge density is a basic quantity that is directly relevant to many phenomena, from surface interactions to DNA hybridization. Measurement and quantification of surface charge density can lead to a better understanding of biomolecular interactions on surfaces. To date, different techniques have been developed to measure surface charge density, including potentiometric titration, atomic force microscopy and reflection interference
Application Note: 110 – Studying Protein Adsorption Properties with SPR
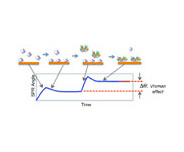
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) can be applied as a convenient, sensitive and label-free technique to study various surface phenomena. One such example is the Vroman effect exhibited by protein adsorption onto surfaces. This important effect arises from the fact that protein adsorption capability onto a surface depends on motility, which is intimately related to its molecular weight. In general, a high molecular weight (HMW) protein adsorbs
Application Note: 109 – Application of SPR to Bacteriology: Endotoxin/Protein Interaction Studies
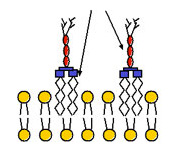
Endotoxin (commonly referred to as lipopolysaccharide in bacteriology) is associated with the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacterial pathogens such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Shigella, and Pseudomonas [1-2]. The interaction between endotoxin and bacterial cell surface is schematically depicted in Figure 1. Endotoxin elicits a series of pleiotropic effects on cells or organisms and is therefore harmful to most mammals
Application Note: 108 – SPR as a Chromatographic Detector: Separation and Label-Free Detection of Biomolecules
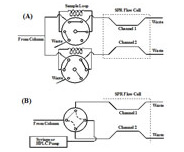
In recent years, SPR has been used as an alternative detector for monitoring elution of a variety of species (e.g., polysaccharides and proteins [1-4]) out of liquid chromatographic (LC) columns. In addition to simplicity and fast speed the SPR detector can detect any eluent, as long as its index of refraction is different from that of the carrier buffer. The open design of the BI-SPR instruments allows users to conveniently connect
